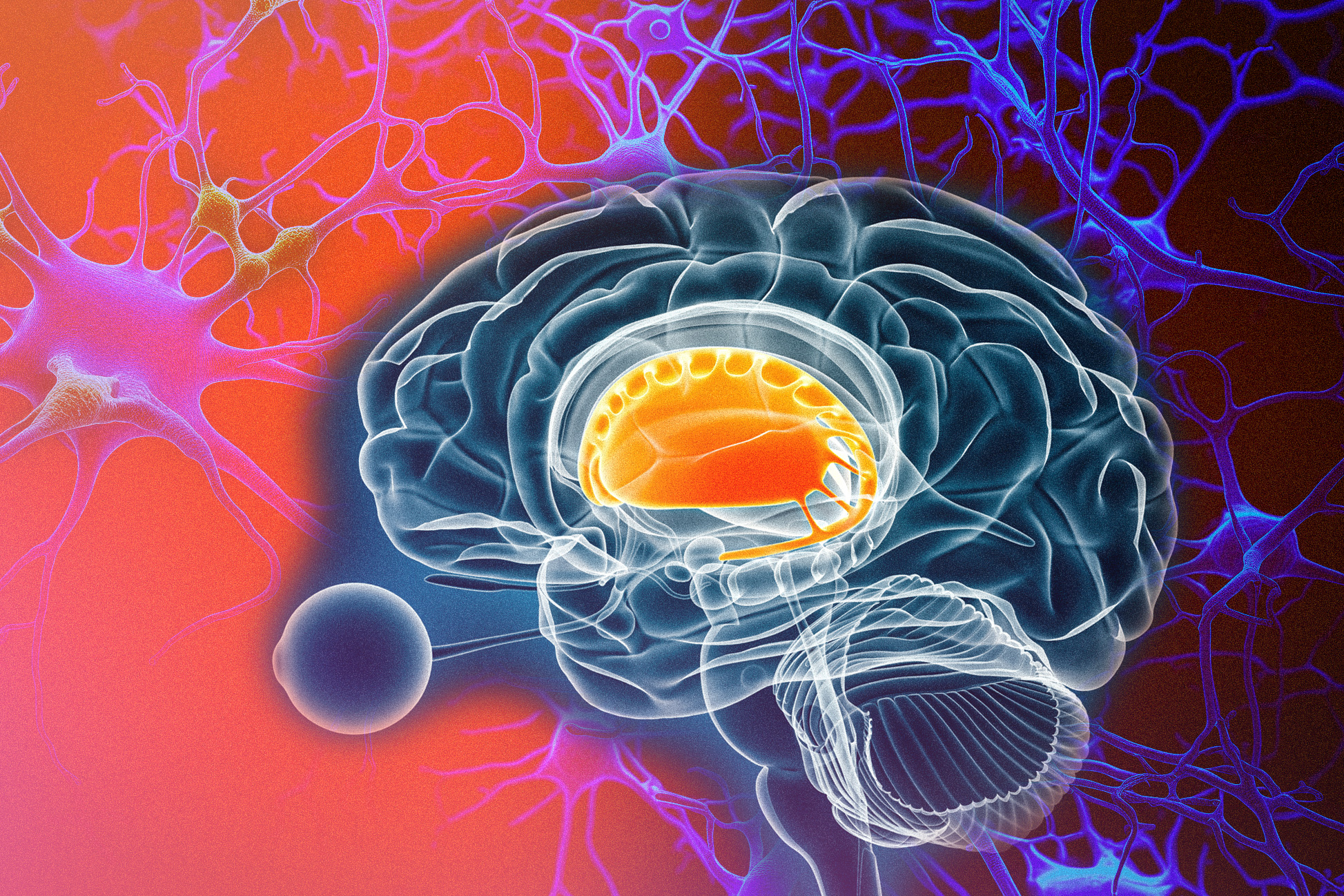
Within the human brain, movement is coordinated by a brain region called the striatum, which sends instructions to motor neurons in the brain. Those instructions are conveyed by two pathways, one that initiates movement (“go”) and one that suppresses it (“no-go”).In a new study, MIT researchers have discovered an additional two pathways that arise in the striatum and appear to modulate the effects of the go and no-go pathways. These newly discovered pathways connect to dopamine-producing neurons in the brain — one stimulates dopamine release and the other inhibits it.By…



