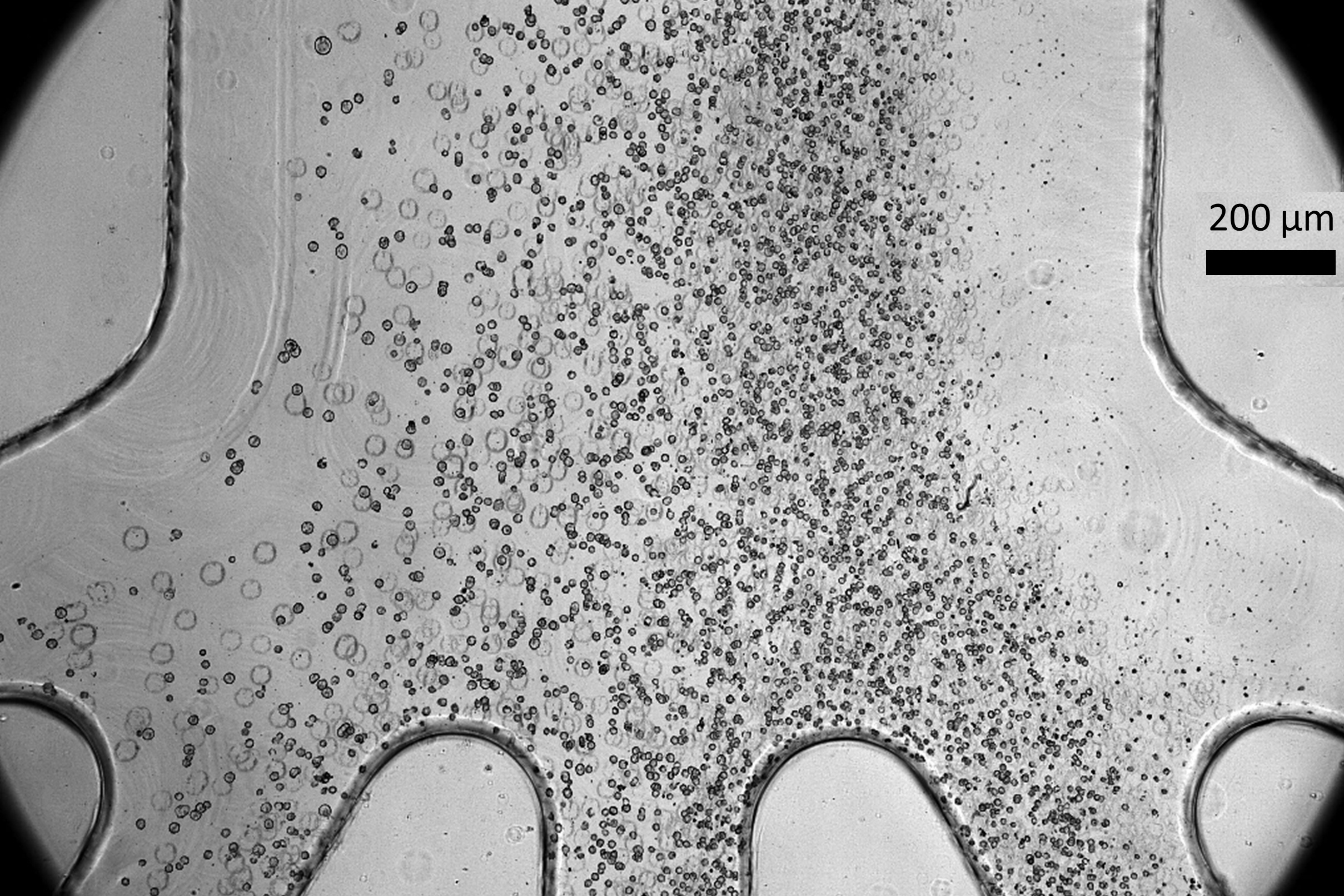
A tiny device built by scientists at MIT and the Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology could be used to improve the safety and effectiveness of cell therapy treatments for patients suffering from spinal cord injuries. In cell therapy, clinicians create what are known as induced pluripotent stem cells by reprogramming some skin or blood cells taken from a patient. To treat a spinal cord injury, they would coax these pluripotent stem cells to become progenitor cells, which are destined to differentiate into spinal cord cells. These progenitors are then…



