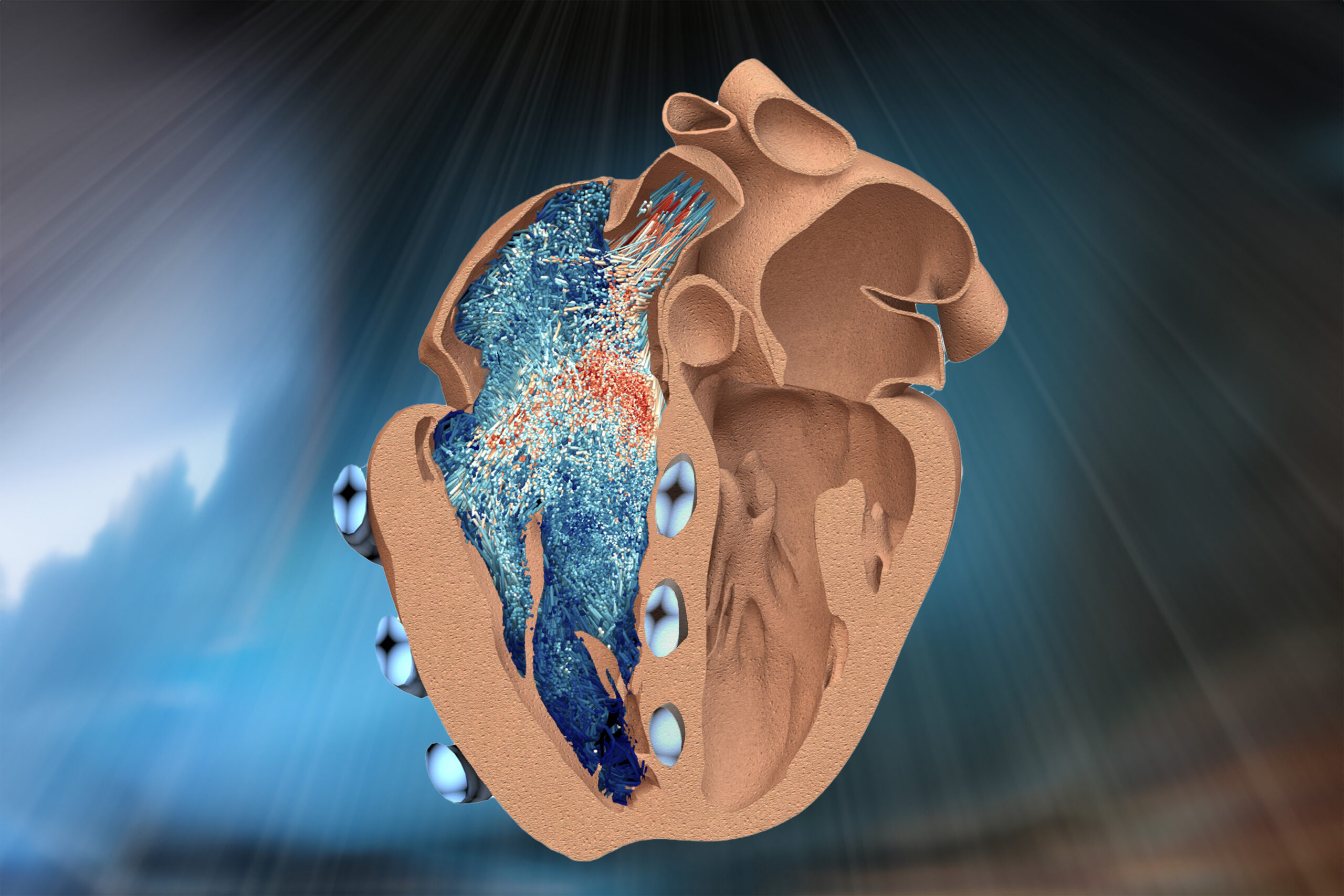
MIT engineers have developed a robotic replica of the heart’s right ventricle, which mimics the beating and blood-pumping action of live hearts. The robo-ventricle combines real heart tissue with synthetic, balloon-like artificial muscles that enable scientists to control the ventricle’s contractions while observing how its natural valves and other intricate structures function. The artificial ventricle can be tuned to mimic healthy and diseased states. The team manipulated the model to simulate conditions of right ventricular dysfunction, including pulmonary hypertension and myocardial infarction. They also used the model to test cardiac…



