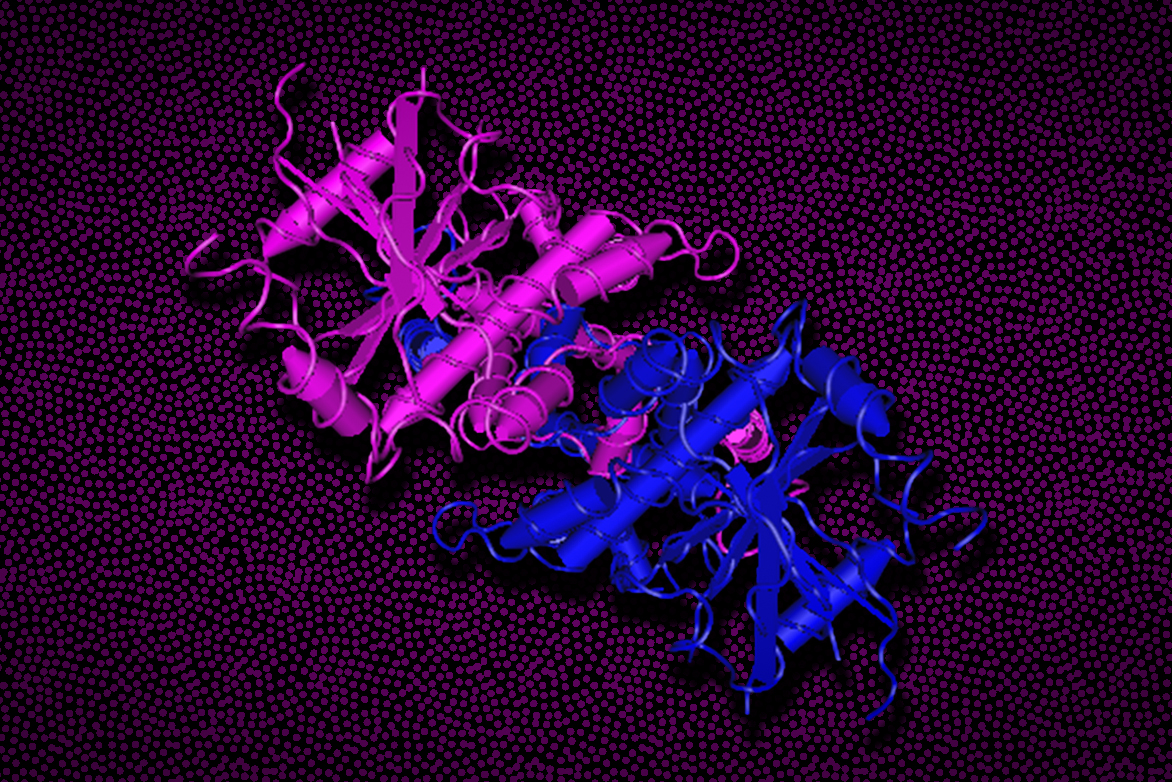
A signaling protein known as STING is a critical player in the human immune system, detecting signs of danger within cells and then activating a variety of defense mechanisms. STING is primarily on the lookout for DNA, which can indicate either a foreign invader such as a virus or damage to the host tissue or cell. When STING detects that danger signal, it can turn on at least three different pathways — one leading to interferon production, one to non-canonical autophagy (involved in recycling cell components and clearing pathogens), and…



