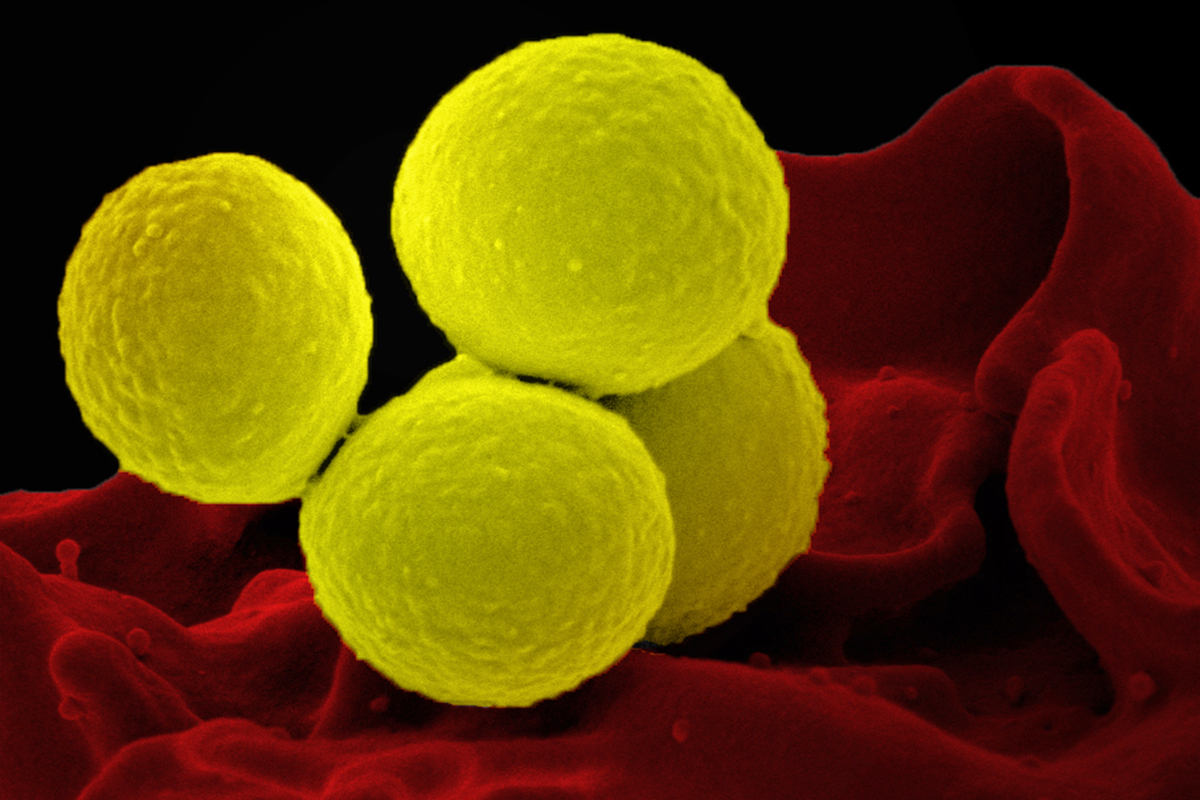
Human skin is home to millions of microbes. One of these microbes, Staphylococcus aureus, is an opportunistic pathogen that can invade patches of skin affected by eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis. In a new study, researchers at MIT and other institutions have discovered that this microbe can rapidly evolve within a single person’s microbiome. They found that in people with eczema, S. aureus tends to evolve to a variant with a mutation in a specific gene that helps it grow faster on the skin. This study marks the first…



