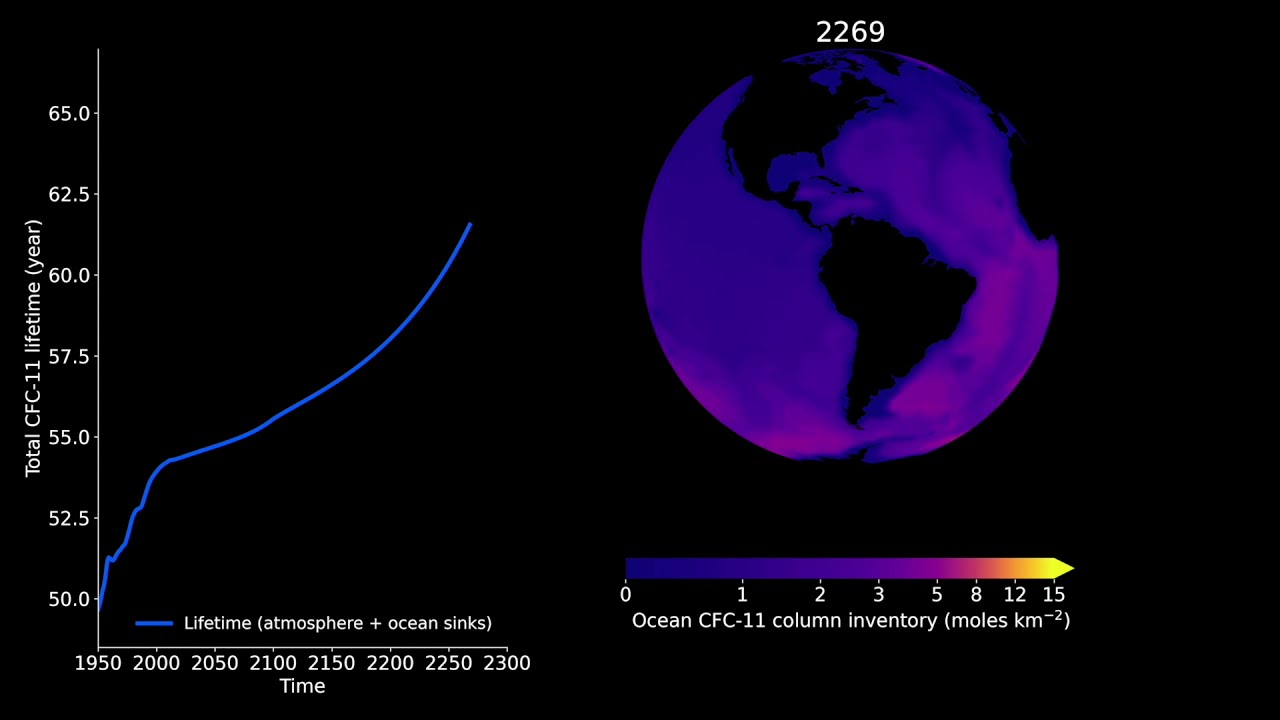
The world’s oceans are a vast repository for gases including ozone-depleting chlorofluorocarbons, or CFCs. They absorb these gases from the atmosphere and draw them down to the deep, where they can remain sequestered for centuries and more. Marine CFCs have long been used as tracers to study ocean currents, but their impact on atmospheric concentrations was assumed to be negligible. Now, MIT researchers have found the oceanic fluxes of at least one type of CFC, known as CFC-11, do in fact affect atmospheric concentrations. In a study appearing today in…



