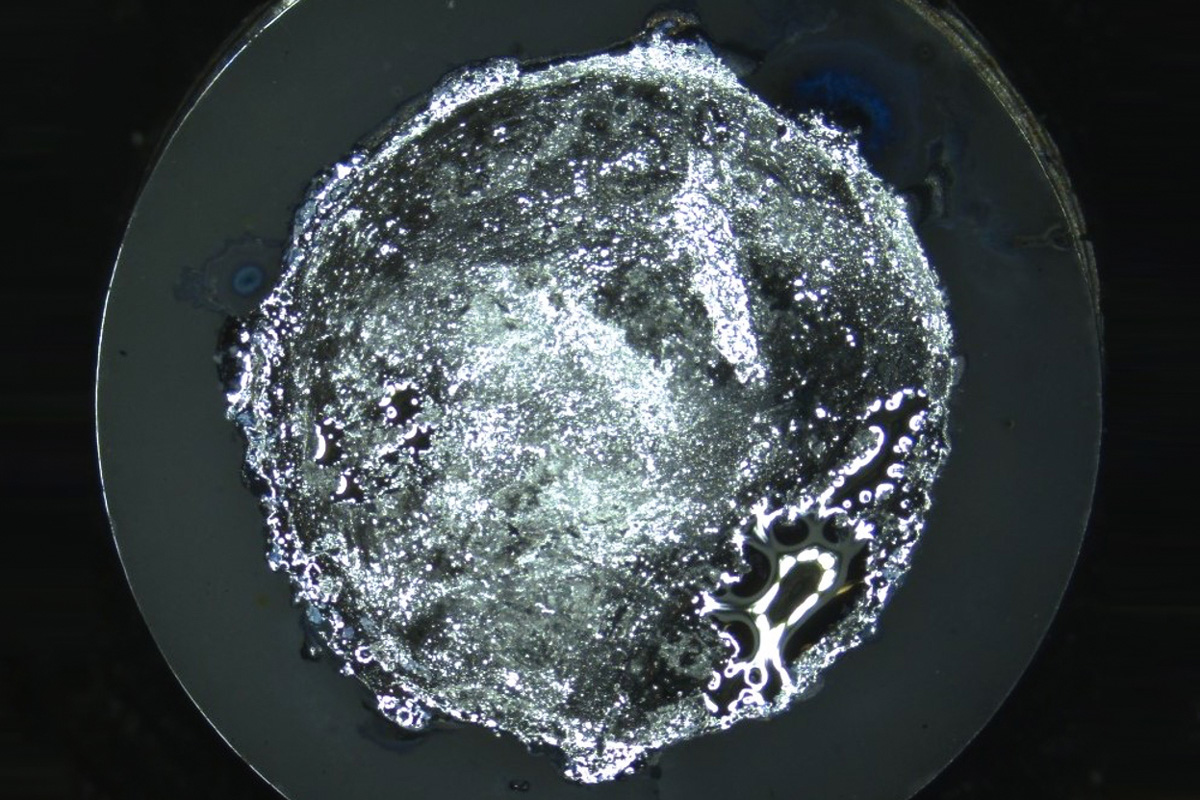
As researchers push the boundaries of battery design, seeking to pack ever greater amounts of power and energy into a given amount of space or weight, one of the more promising technologies being studied is lithium-ion batteries that use a solid electrolyte material between the two electrodes, rather than the typical liquid. But such batteries have been plagued by a tendency for branch-like projections of metal called dendrites to form on one of the electrodes, eventually bridging the electrolyte and shorting out the battery cell. Now, researchers at MIT and…



