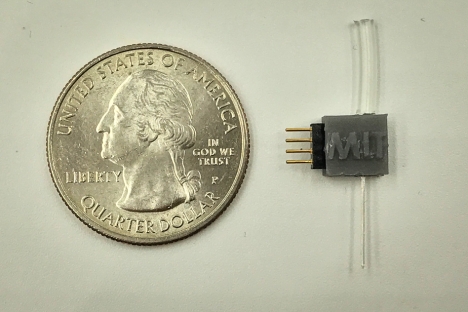
Nitric oxide is an important signaling molecule in the body, with a role in building nervous system connections that contribute to learning and memory. It also functions as a messenger in the cardiovascular and immune systems. But it has been difficult for researchers to study exactly what its role is in these systems and how it functions. Because it is a gas, there has been no practical way to direct it to specific individual cells in order to observe its effects. Now, a team of scientists and engineers at MIT…



