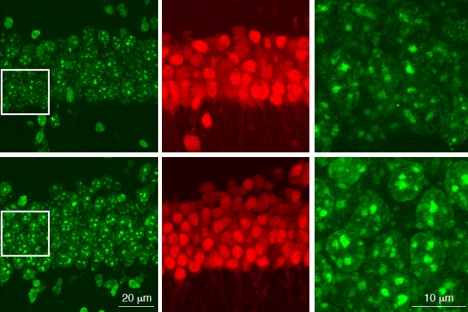
MIT neuroscientists have discovered that an enzyme called HDAC1 is critical for repairing age-related DNA damage to genes involved in memory and other cognitive functions. This enzyme is often diminished in both Alzheimer’s patients and normally aging adults. In a study of mice, the researchers showed that when HDAC1 is lost, a specific type of DNA damage builds up as the mice age. They also showed that they could reverse this damage and improve cognitive function with a drug that activates HDAC1. The study suggests that restoring HDAC1 could have…



