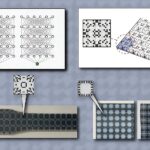
Automated method helps researchers quantify uncertainty in...
Pollsters trying to predict presidential election results and physicists searching for distant exoplanets have at least one thing in common: They often use a tried-and-true scientific technique called Bayesian inference. Bayesian inference allows these scientists to effectively estimate some unknown parameter — like the winner of an election — from data such as poll results. But Bayesian inference can be slow, sometimes consuming weeks or even months of computation time or requiring a researcher to spend hours deriving tedious...