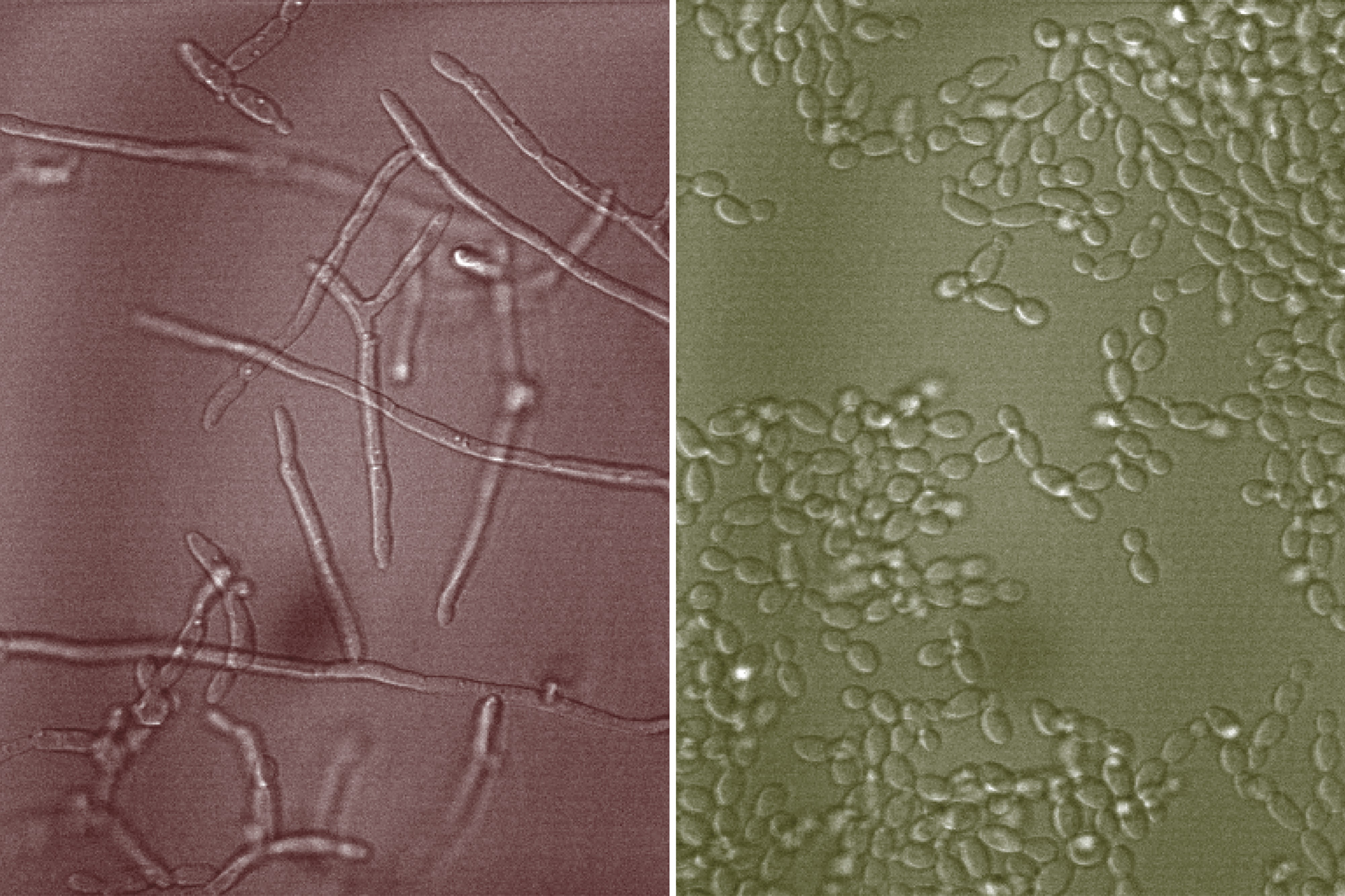
Candida albicans is a yeast that often lives in the human digestive tract and mouth, as well as urinary and reproductive organs. Usually, it doesn’t cause disease in its host, but under certain conditions, it can switch to a harmful form. Most Candida infections are not lethal, but systemic Candida infection, which affects the blood, heart, and other parts of the body, can be life-threatening. MIT researchers have now identified components of mucus that can interact with Candida albicans and prevent it from causing infection. These molecules, known as glycans,…



