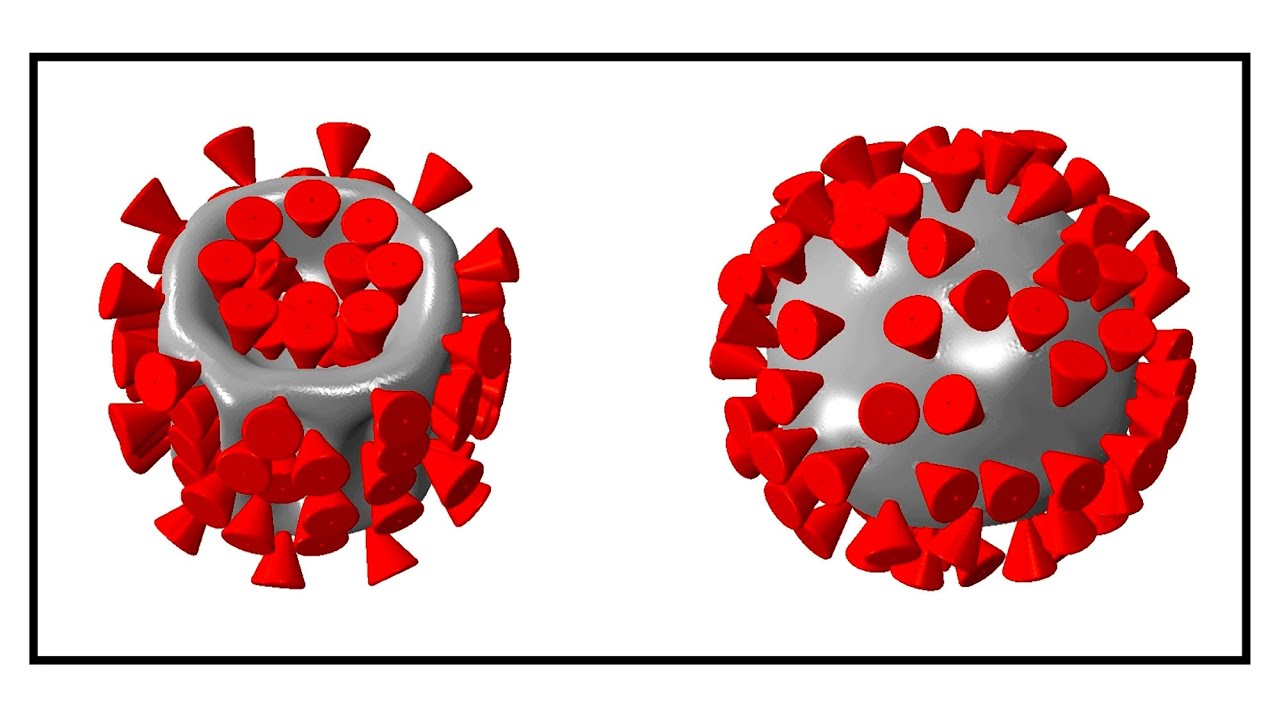
The coronavirus’ structure is an all-too-familiar image, with its densely packed surface receptors resembling a thorny crown. These spike-like proteins latch onto healthy cells and trigger the invasion of viral RNA. While the virus’ geometry and infection strategy is generally understood, little is known about its physical integrity. A new study by researchers in MIT’s Department of Mechanical Engineering suggests that coronaviruses may be vulnerable to ultrasound vibrations, within the frequencies used in medical diagnostic imaging. Through computer simulations, the team has modeled the virus’ mechanical response to vibrations across…



