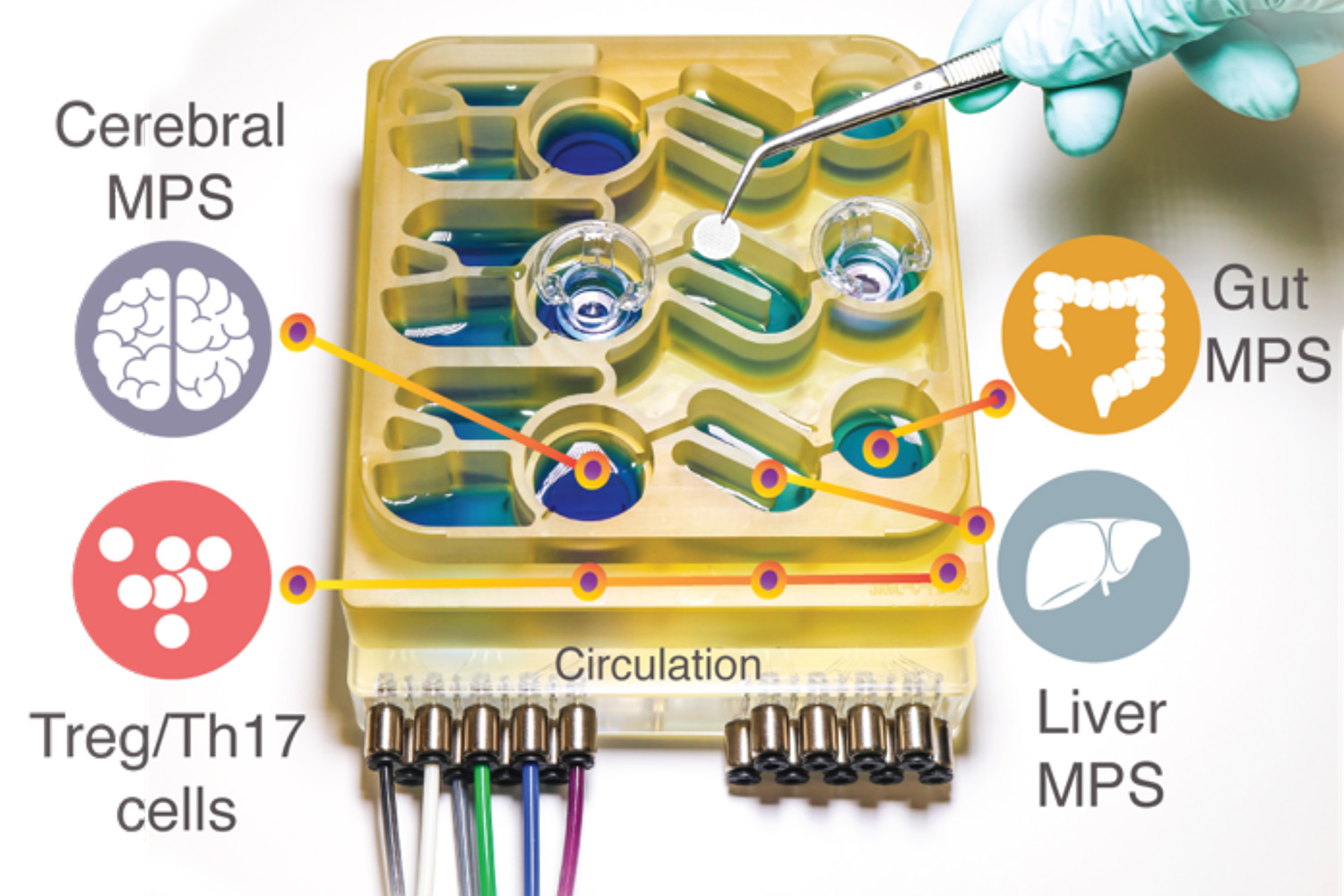
In many ways, our brain and our digestive tract are deeply connected. Feeling nervous may lead to physical pain in the stomach, while hunger signals from the gut make us feel irritable. Recent studies have even suggested that the bacteria living in our gut can influence some neurological diseases. Modeling these complex interactions in animals such as mice is difficult to do, because their physiology is very different from humans’. To help researchers better understand the gut-brain axis, MIT researchers have developed an “organs-on-a-chip” system that replicates interactions between the…



