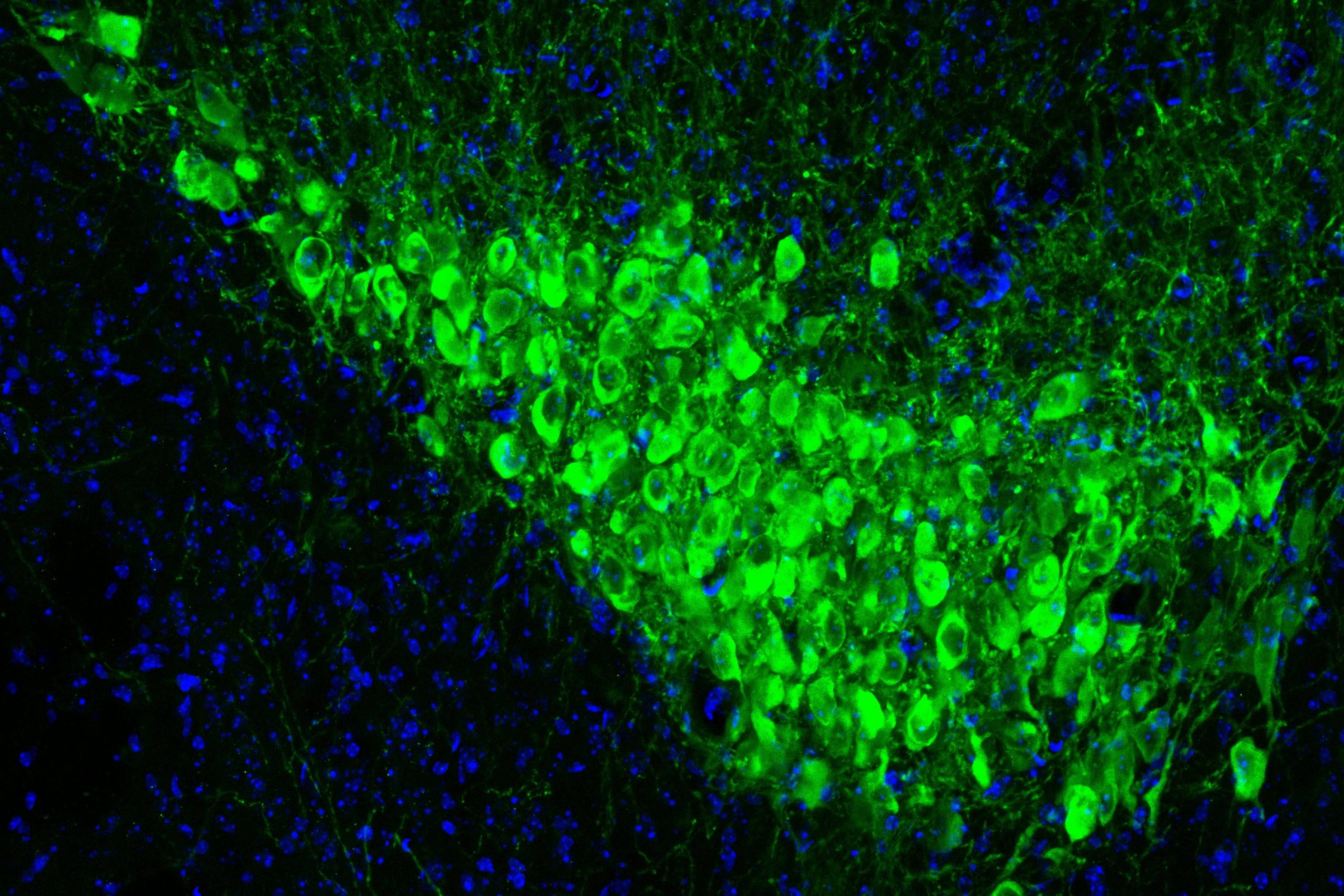
The attentional control that organisms need to succeed in their goals comes from two abilities: the focus to ignore distractions and the discipline to curb impulses. A new study by MIT neuroscientists shows that these abilities are independent, but that the activity of norepinephrine-producing neurons in a single brain region, the locus coeruleus, controls both by targeting two distinct areas of the prefrontal cortex. “Our results demonstrate a fundamental causal role of LC neuronal activation in the implementation of attentional control by the selective modulation of neural activity in its…



