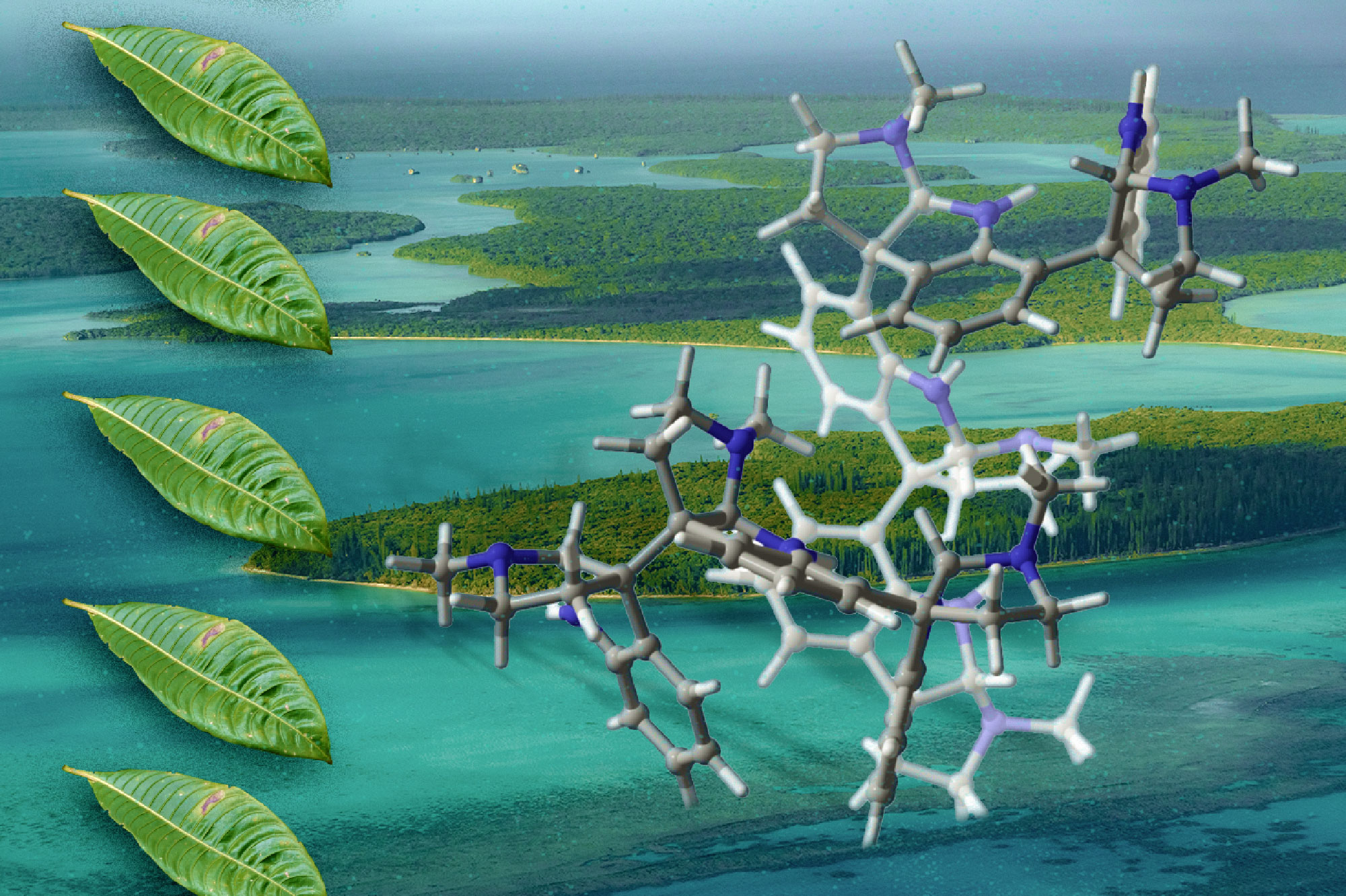
MIT chemists have developed a new way to synthesize complex molecules that were originally isolated from plants and could hold potential as antibiotics, analgesics, or cancer drugs.These compounds, known as oligocyclotryptamines, consist of multiple tricyclic substructures called cyclotryptamine, fused together by carbon–carbon bonds. Only small quantities of these compounds are naturally available, and synthesizing them in the lab has proven difficult. The MIT team came up with a way to add tryptamine-derived components to a molecule one at a time, in a way that allows the researchers to precisely assemble…



