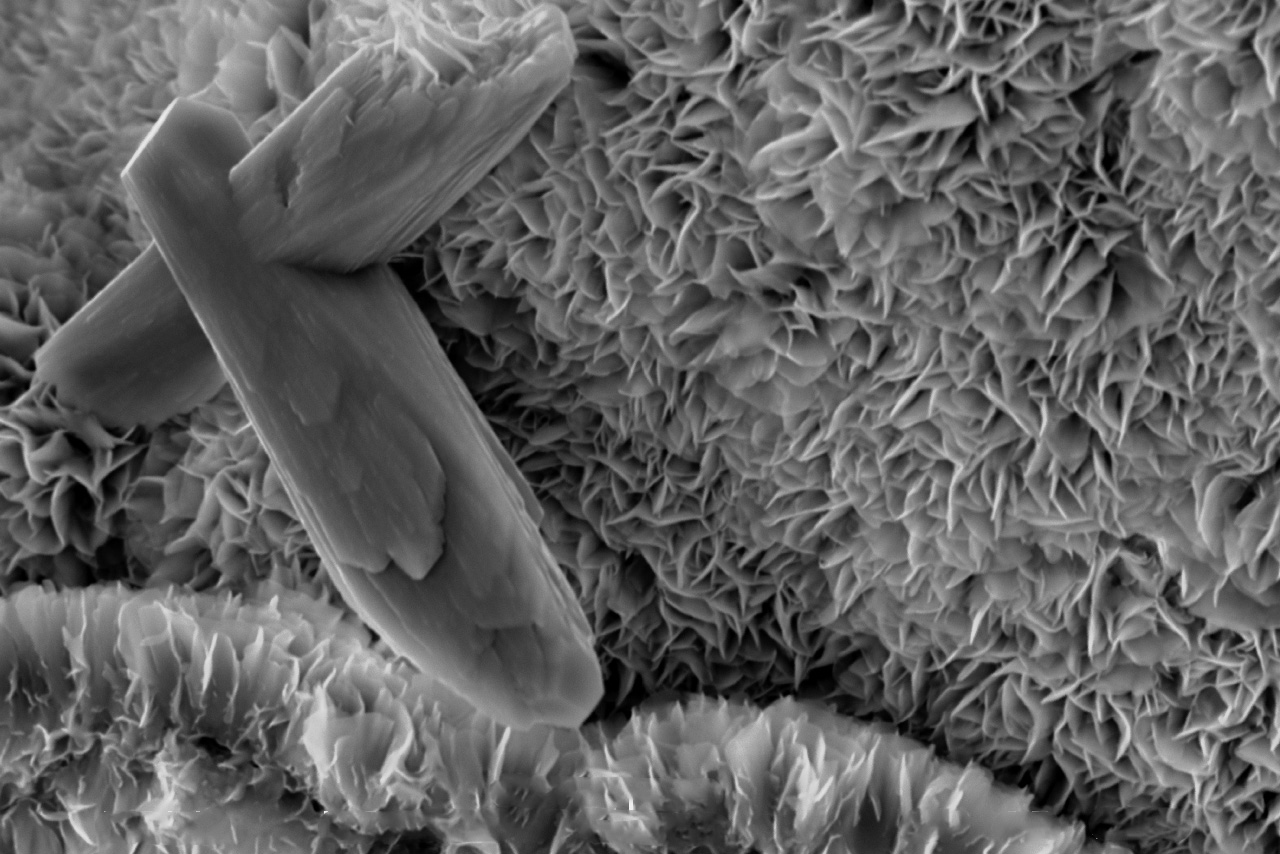
MIT geologists have found that a clay mineral on the seafloor, called smectite, has a surprisingly powerful ability to sequester carbon over millions of years. Under a microscope, a single grain of the clay resembles the folds of an accordion. These folds are known to be effective traps for organic carbon. Now, the MIT team has shown that the carbon-trapping clays are a product of plate tectonics: When oceanic crust crushes against a continental plate, it can bring rocks to the surface that, over time, can weather into minerals including…



